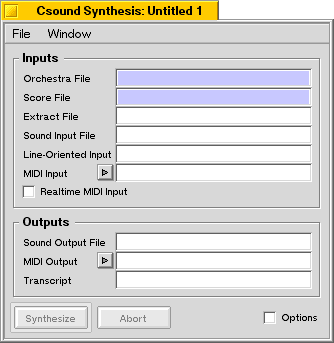
The synthesis window provides controls for running Csound in its normal mode, processing input files describing a set of instruments (an orchestra) and a sequence of events directing those instruments (a score). Optionally, the synthesis process can also be driven by a MIDI file, or by realtime events from a number of sources.
There are a lot of options for sound synthesis; most of them are accessible via a separate options window. The following controls are present in the main synthesis window:
- Orchestra File
- The name of the file containing definitions of the instruments
used for sound synthesis. See the Csound documentation for a description
of the orchestra language.
This is a mandatory entry field. - Score File
- The name of the file containing a list of events and waveforms which will
drive the synthesis process. The file must be in standard numeric
score format; SCOT format is no longer supported.
This is a mandatory entry field. - Extract File
- If given, this file name is passed to Csound to specify that only a part of the score file should be processed. The format of extract files is documented in the Csound manual.
- Sound Input File
- If the orchestra contains instruments which use the sound input opcodes
in,insorinq, they will read from the file specified in this entry field. Realtime sound input is possible by entering eitheradcordevaudio.[1]
NOTE: The Csound Shell does not permit data to be read from the standard input stream; the file name must be given if the orchestra uses the sound input opcodes. - Line-Oriented Input
- The value of this field, if given, is passed to Csound as the argument of
the
-Lcommand-line option. Csound will read note events in standard numeric score format from this file and process them as if they came from the score file. Realtime processing is possible by entering the name of an input device (like/dev/ports/serial1on a BeBox). - MIDI Input
- Csound can read and process MIDI events. It will read them from the file
(or device) named by this entry field. The small button pops up a menu of
MIDI producers which are available for use.
NOTE: When reading MIDI events, there should be anf0statement in the score file, otherwise synthesis may end before all MIDI data have been processed. See the Csound manual for details. - Realtime MIDI Input
- If this option is selected, Csound expects the MIDI data to come from a real
MIDI source.[1] If this option is not selected,
Csound expects input to come from a MIDI file in one of two formats: standard
MIDI file format 0 (single track) or MPU401 format.
See the chapter on MIDI Support for a description of realtime MIDI processing in BeOS. - Sound Output File
- Csound writes its synthesized output into the file named by this entry
field. If no file name is given, Csound uses a default
("
test"). A value of eitherdevaudioordacselects realtime output.[1]
NOTE: Output to the standard output stream is not really useful when using the Csound Shell. - MIDI Output
- Although Csound's main purpose is the synthesis of sounds, newer versions
can also output MIDI events (with a suitable orchestra file). The MIDI events
are directed at the MIDI consumer named by this entry
field.[1] The small button pops up a menu of MIDI
consumers which are available for use.
See the chapter on MIDI Support for a description of realtime MIDI processing in BeOS. - Transcript
- If this entry field contains a filename, all messages printed by Csound are logged and written to the named file.
- Synthesize
- Clicking on this button (when enabled) starts Csound in its synthesis mode.
- Abort
- Clicking on this button (when enabled) causes a running synthesis to be aborted.
- Options
- Shows resp. hides the synthesis options window.
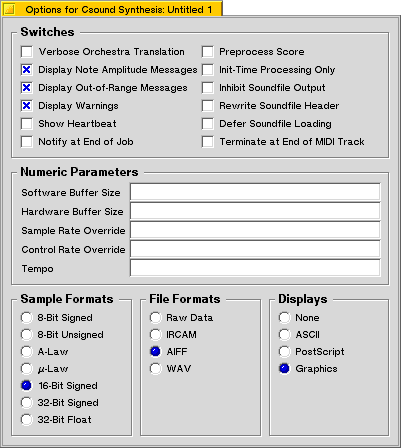
A synthesis options window is always associated with a synthesis window, and its controls have effect on the job associated with that window. For this reason, a synthesis options window has no menu and does not provide a means to start Csound execution.
Controls in the synthesis options window are grouped according to their type.
- Verbose Orchestra Translation
- Causes Csound to print detailed messages about translation and performance (useful for debugging an orchestra).
- Display Note Amplitude Messages
- If switched on, each note being processed produces a message containing its time, duration and amplitude.
- Display Out-of-Range Messages
- Controls warnings about output samples which had to be clipped because they exceeded the range representable by the selected sample format.
- Display Warnings
- Enables various warning messages.
- Show Heartbeat
- Causes a "heartbeat" character to be printed each time a block of samples is written to the output file.
- Notify at End of Job
- Signals the end of processing via an acoustic signal.
- Preprocess Score
- If switched on, the score will be preprocessed by
cscore. This requires a version of Csound which has the desiredcscoreroutine compiled in. It won't work with the default executable. - Init-Time Processing Only
- Causes Csound to only process init-time statements in the orchestra. No samples are produced and no output file is generated.
- Inhibit Soundfile Output
- Causes the synthesized sound samples to be discarded.
- Rewrite Soundfile Header
- When selected, the output file's header (if any) is rewritten each time a block of samples is appended to the file. This makes the file playable even if Csound is aborted before synthesis is complete.
- Defer Soundfile Loading
- Controls the time at which soundfiles will be loaded by
GEN01statements in the score. Normally they are loaded when the function-table is created; if this option is switched on, loading is deferred until performance time. - Terminate at End of MIDI Track
- Causes synthesis to end after the last MIDI event has been processed.
When synthesizing from MIDI, the score usually just contains function table
data and an
f0statement long enough to allow the whole MIDI track to be processed. Unless this option is selected, the output file will be padded with zeroes until it has the length determined by the score.
- Software Buffer Size
- Size of the buffer used to accumulate samples during synthesis. The default
value (used if the field is left empty) is 1024 sample frames.
If a negative number -N is given, the buffer size will be
N * ksmps, where ksmps is the number of samples per control
period defined by the orchestra.
This parameter also affects realtime audio I/O; see the Csound manual for details. - Hardware Buffer Size
- Number of sample frames in the realtime I/O (ADC/DAC) buffer. The default
value is 1024; it can be tuned to reduce latency (using smaller values) or
dropouts (using larger buffers). See the Csound manual for details.
- Sample Rate Override
- Overrides the orchestra's
srparameter. The sample and control rate must be either both left alone, or both overridden. The sample rate must be divisible by the control rate. - Control Rate Override
- Overrides the orchestra's
krparameter. See previous item. - Tempo
- Sets the initial tempo used to process the score, and allows the tempo to
be controlled from the orchestra using the
tempoopcode. The value is given in beats per minute.
- 8-Bit Signed
- Signed bytes (-128 .. 127).
- 8-Bit Unsigned
- Unsigned bytes (0 .. 255). Offset by 128 relative to the signed format.
- A-Law
- Samples compressed to 8 bits using the "A-Law" compression function
(Reference: CCITT Recommendation G.711).
- µ-Law
- Samples compressed to 8 bits using the "µ-Law" ("Mu-Law", "U-Law") compression function (Reference: CCITT Recommendation G.711).
- 16-Bit Signed
- Signed 2-byte integers (-32768 .. 32767). This is the default format.
- 32-Bit Signed
- Signed 4-byte integers (-2147483648 .. 2147483647).
- 32-Bit Float
- Single-precision IEEE floating-point numbers (ca. 1.2e-38 .. 3.4e+38).
- Raw Data
- The output file does not contain any header or format information.
- IRCAM
- The output file contains an IRCAM soundfile header (unless Csound has been built with a different default soundfile format).
- AIFF
- The output file will be in AIFF format.
NOTE: If the selected sample format is 32-Bit Float, the output will actually be an AIFC file. If the selected sample format is not legal for an AIFF file, a different sample format will be substituted. - WAV
- The output file will be in WAV format.
NOTE: If the selected sample format is not legal for a WAV file, a different sample format will be substituted.
- None
- No diagrams will be generated. This is the fastest option.
- ASCII
- ASCII graphics will be sent to the standard output stream.
- PostScript
- Embedded PostScript diagrams will be written to a file in the same
directory as the output file, with the output file's base name and the
extension
eps. - Graphics
- Diagrams are displayed in windows.[2]
[1] All realtime sound or MIDI support requires that the Csound Server is running.
[2] Graphical displays are possible only when the Csound Server is running.