This section explains how Microsoft NNTP Service works. It describes:
Microsoft NNTP Service implements NNTP, which is a client/server protocol. Microsoft NNTP Service functions as the server; Microsoft Internet Mail and News is an example of a typical client.
Clients connect to Microsoft NNTP Service through a Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) network. For normal connections, the default TCP port is 119; for optional encrypted SSL connections, the default TCP port is 563.
Microsoft NNTP Service runs as a service on Windows NT Server and is configured to start automatically. The service name in the Services application in Control Panel is Microsoft NNTP Service.
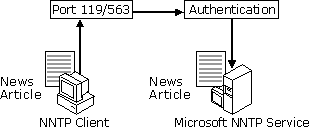
You post newsgroup articles to Microsoft NNTP Service using a news client such as Microsoft Internet Mail and News. The client connects to Microsoft NNTP Service and requests that an article be posted to one or more newsgroups. Microsoft NNTP Service receives the connection request and verifies the user's authorization to post to the specified newsgroups. Microsoft NNTP Service then adds the article to the newsgroups and updates the newsgroup index. The figure below illustrates this process.

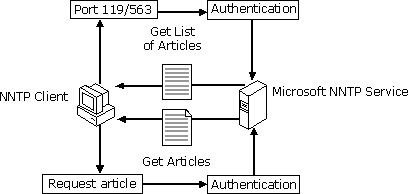
You view newsgroup articles on Microsoft NNTP Service using a news client such as Microsoft Internet Mail and News. The first step in viewing newsgroup articles is getting a list of available newsgroups. The client connects to Microsoft NNTP Service and requests the list of available newsgroups. Microsoft NNTP Service receives the connection request, verifies that user access to newsgroups is authorized, and then sends the client a list of all available newsgroups.
The second step is selecting the newsgroup the user wants to view. The client requests the list of articles for the selected newsgroup. Microsoft NNTP Service verifies that user access to the specified newsgroup is authorized and sends the client a list of all articles in that newsgroup. Then as the user selects articles, the client requests the articles from Microsoft NNTP Service, and Microsoft NNTP Service returns the contents of the articles. The figure below illustrates the steps in this process.
Microsoft NNTP Service stores newsgroup articles in one or more directory hierarchies. Each newsgroup has its own directory, and each article is stored as a file in that directory.
The main directory is C:\Inetpub\Nntproot by default, which can be changed in the Home Directory property sheet of Microsoft NNTP Service. You can create additional directory hierarchies on other disk drives or other computers by creating virtual directories.
The newsgroup directory has the same name as the newsgroup. Microsoft NNTP Service automatically creates the required directories when you create new newsgroups. For example, the newsgroup named entertainment.news is stored in the directory \Entertainment\News under the root directory C:\Inetpub\Nntproot\Entertainment\News by default. All newsgroup article files have an .nws extension.
Microsoft NNTP Service also creates files that list the subjects of the stored articles; these files have an .xix extension. Microsoft NNTP Service creates one of these subject files for every 128 articles in a newsgroup.
Microsoft NNTP Service also maintains a number of internal data structure files with .hsh, .hdr, .lst, and .txt extensions. The default location of these files is C:\Inetpub\Nntpfile. Do not modify or delete these files. Rebuilding Microsoft NNTP Service restores these files if they are accidentally deleted or damaged.