


The Ruled Surface tool is used to create a surface between two or more 2D or 3D curves. An example of a ruled surface would be the wing of an airplane: the structural members of the wing represent the curves and the wing’s surface is the mesh linking those curves together. |
| |
A Ruled Surface can be built either in NURBS mode or in polygonal mode. | ||
|
| |
Ruled Surface with polygonal curves |
Ruled Surface with NURBS curves | |
q Between curves
Usage:
1. Creating the 2D or 3D curves.
The curves may have different profiles and a different number of points. Amapi 3D will automatically interpolate the missing points.
![]()
The only constraint is that the curves must all either be open or closed. You can not create a ruled surface between an open curve and a closed curve.
2. Select the Ruled Surface tool.
Click on the icon depicting the Ruled Surface tool in the Tools Palette.
3. Selecting a point on each curve.
Amapi 3D draws a segment between the two curves selected and uses it to create the surface. Therefore, choose the points carefully. Results will vary depending on the points you select.
Þ Click on a point of the 1st curve.
Þ Click on a point of the 2nd curve.
Þ Do the same for all the other curves. A flat surface, or “skin” is created between each curve.
Þ Press the Return key to end the selection process.
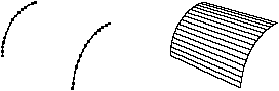
4. Capping the openings.
If the curves used were closed curves, a closed surface with two openings (highlighted in red) is created. Click on the opening you wish to close using the Wand. Or go to the next step if you want to leave them open.
5. Ending the tool action.
Validate or put the tool aside to end the tool action (depending on the interface). See chapter User Manual/Tools/Generic use of a tool/How do you end a tool action?
![]()
The construction curves used are sent in the hidden scene. Use the Unhide tool to bring them back in the main scene if necessary.
|
Practical exercises: · A windshield for a motorbike/(2nd method: ruled surface)/Step 2
|
q Ruled surfaces between surfaces
You can create a surface between two existing surfaces. A surface is an object with open faces (no closed volumes)
Usage:
1. Select the edge of an open face or a point on a curve.
2. Select a point on the edge of an open face of another object.
3. The surface is built between both objects.
|
|
![]()
In this case, the choice of the points selected is important; the two points define the starting point of the action.