Calculator Basics
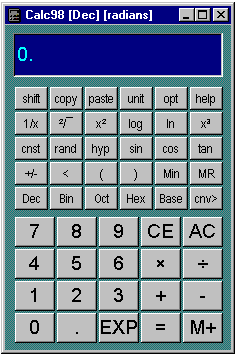
As you would expect, you use the calculator just as you would a real
pocket calculator. Just as with a conventional calculator, space is at
a premium, so many of the calculator buttons have to double up the functions
they provide. The layout of the calculator in its normal state has the
functions you would expect to see on a fairly standard scientific calculator,
which means that it is probably self explanatory. Notice the shift
button in the top left hand corner.
Enter numbers either by clicking on the buttons or using the keyboard
(note: to use a numeric keypad make sure Num Lock is on). To enter a number
in exponential format, enter the mantissa, followed by the EXP key,
then +/- if required, then the exponent. To use the arithmetic functions,
click their buttons. If the function is unary (i.e. acts on one number,
e.g. 1/x) the display is updated to the result. If the function
is binary (e.g. +, -, X etc.) enter the second number
and click = or another arithmetic key.
The functions of the buttons in their shifted state are not marked on
the calculator body, but the buttons change when you press the shift
button. If you press the shift button again, the buttons revert
to their un-shifted state.
Most of the calculator buttons can be accessed from your computer keyboard
(these are sometimes called 'keyboard shortcuts' or 'keyboard accelerators').
Keyboard accelerators are listed by key and
by meaning. You can also use the Caps Lock key
on your keyboard instead of the shift button.
An optional menu bar (or command bar) can be used to give access to
additional functions. All the menu bar functions can be obtained in other
ways. Activate the menu bar using the Layout tab
of the Options dialog.
 - All Clear
- All Clear
Clears the calculator, and resets any functions. The contents of the memory
are not affected by AC. The memory can be cleared after pressing
AC
by pressing Min.
 - Clear Entry
- Clear Entry
Erases the last number or operation entered.
 - Addition
- Addition
This button performs addition.
 - Minus
- Minus
This button performs subtraction.

 - Divide
- Divide
This button performs division.

 - Multiply
- Multiply
This button performs multiplication.
 - Equals
- Equals
Displays the result of an arithmetic operation. It can be used during a
calculation to ensure that an intermediate result has been evaluated. Unless
the = button is pressed, it is possible that an operation is incomplete
- pressing = ensures that no arithmetic operations are pending.
Certain functions make use of the = button to signify the end
of input, in order to evaluate a result.
 - Percent key
- Percent key
This button (
 or Enter button) displays the result of an arithmetic operation as a percentage.
or Enter button) displays the result of an arithmetic operation as a percentage.
Examples:
Calculate five sixteenths as a percentage.
5 / 1 6 shift %
Result: 31.25%
Calculate 17.5% of £25.00:
250 x 17.5 shift %
Result: £43.75
Calculate 12% mark-up on $250
250 + 12 shift %
Result: $280
Give 5% discount on goods costing $125
125 - 5 shift %
Result: $118.75
 - Pi key
- Pi key
This button (shifted Exp button) displays the value of pi (the ratio of
the circumference of a circle to its diameter).
 - Memory Plus
- Memory Plus
Pressing this button adds the number displayed to the contents of the memory.
Additional memories can be accessed by pressing the shift key before
pressing this button, which will change to Mn+.
 - Memory n
Plus
- Memory n
Plus
Add to one of ten memories (labelled 0-9) using this button, which is obtained
by pressing the shift button. After pressing Mn+ press the
number button corresponding to the desired memory. Memory number zero is
the default memory (i.e. the memory referred to by the un-shifted memory
buttons).
 - Memory Input
- Memory Input
Press the min button to enter the currently displayed number into
the memory.
If you first press shift before Min you can select one
of the ten memories (0-9). Memory zero is the default memory, i.e. the
memory available without pressing the shift button.
 - Memory n Input
- Memory n Input
Input a value to one of ten memories (labelled 0-9) using this button,
which is obtained by pressing the shift button. After pressing MnIn
press the number button corresponding to the desired memory. Memory number
zero is the default memory (i.e. the memory referred to by the un-shifted
memory buttons). The "Clear All" button allows you to delete the contents of all
the memories.
 - Memory Recall
- Memory Recall
Use this button to put the contents of the memory onto the display. The
default memory is number zero. To display other memories, first press the
shift button and then the MR button and select the required
memory.
 - Memory n Recall
- Memory n Recall
Access one of ten memories (labelled 0-9) using the this button, which
is obtained by pressing the shift button. After pressing MnR
press the number button corresponding to the desired memory. Memory number
zero is the default memory (i.e. the memory referred to by the un-shifted
memory buttons).
 - Decimal Point
- Decimal Point
Use the point button to enter the decimal part of a number. The
decimal point is disabled in non-decimal number systems.
 - Exponent
- Exponent
Use this button to enter a number in exponential form.
Example:
To enter the number 1.234 x 10^6 (1.234E6) press the following buttons:
1 . 2 3 4 EXP 6
 - Number buttons
- Number buttons
Number buttons are used in all modes. In Hexadecimal mode they are augmented
by the letters A to F. In Octal mode the 8 and 9 buttons are disabled.
In Binary mode only the numbers 0 and 1 are enabled. In statistics mode
the number buttons are used with the shift button to obtain the
statistical functions.
 - Shift
- Shift
Use to access additional functions. The functions available depend on the
calculator mode, and are indicated by changes to the legends on the calculator
buttons.
Errors
If you get an error, the calculator display will contain an appropriate
message, and possibly some further descriptive information. In the case
of certain errors, the calculator functions are disabled and you need to
press the AC button to clear the error.