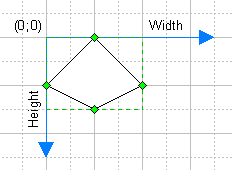
Transform section.
This section contains parameters which define the position,
size and orientation of the object.
Note, that the coordinate system is based on the alignment box of
the object: the coordinate origin is in the top left-hand corner,
horizontal coordinates increase as you move from left to right,
and vertical coordinates increase as you move from top to bottom.

Since an object may be part of a parent group, the following parameters describe its position within the group (relatively to the coordinate system of the group):
OriginX, OriginY, └ngle, LocPinX, LocPinY for a 2D object
BeginX, BeginY, EndX, EndY, Angle, LocPinX, LocPinY for a 1D
object.
Note, that if an object isn't part of any parent group, the program considers that it belongs to the group formed by the entire page.
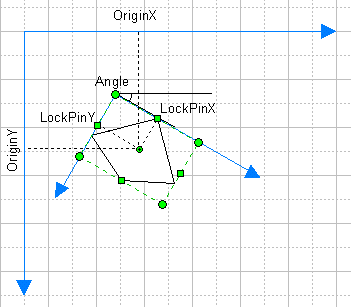
Here are the fields of the section:
Width.
Describes the width of the alignment box of the object. In the
Formulas mode, you see the data in tenths of millimetres, in the
Values mode all data is displayed in the current unit of measure.
As a rule, the Width parameter is used as a variable in formulas
for other fields.
The 1D objects usually have the formula in this field:
_HYP(EndX-BeginX;EndY-BeginY).
If the object is part of a group, its width is described through
the width and height of the parent group. For example:
_HYP(Parent.Width*0.308575;Parent.Height*0.283963).
Height.
Describes the height of the alignment box of the object. In
the Formulas mode, you see the data in tenths of millimetres, in
the Values mode the data is displayed in the current unit of
measure.
As a rule, the Height parameter is used as a variable in formulas
for other fields.
Usually there is a number in this field. If the object is part of a group, its height is described through the width and height of the parent group. For example: _HYP(Parent.Width*0.267234;Parent.Height*0.081973).
Angle.
The angle of the object with respect to its parent group. Describes the width of the alignment box of the object. In the Formulas mode, you see the angle in radians, in the Values mode the angle is displayed in degrees. The angle value may range from -180 deg to 180 deg.
The 1D objects usually have the formula for the angle: FlipX*_PI()+_ATAN2(EndY-BeginY;EndX-BeginX).
OriginX.
Specifies the X offset of the rotation centre of the object with respect to its parent group. In the Formulas mode, you see the data in tenths of millimetres, in the Values mode the data is displayed in the current unit of measure.
OriginY.
Specifies the Y offset of the rotation centre of the object with respect to its parent group. In the Formulas mode, you see the data in tenths of millimetres, in the Values mode the data is displayed in the current unit of measure.
LocPinX.
Describes the X offset of the rotation centre of the object
relatively the coordinate origin of the object. In the Formulas
mode, you see the data in tenths of millimetres, in the Values
mode the data is displayed in the current unit of measure.
The default formula is Width*0.5
LocPinY.
Describes the Y offset of the rotation centre of the object
relatively the origin of the object. In the Formulas mode, you
see the data in tenths of millimetres, in the Values mode the
data is displayed in the current unit of measure.
The default formula is Height*0.5
FlipX.
The flag for horizontal flipping. This is a binary value:
FALSE - the object isn't flipped ;
TRUE - the object is flipped;
FlipY.
The flag for vertical flipping. This is a binary value:
FALSE - the object is flipped;
TRUE - the object isn't flipped. á