ASP Lesson 1: Databases
A very useful function of Active Server Pages is the ability to create, delete, retrieve, and update information within databases. In this class we will be using Microsoft Access databases as our datasource so it is important for you to understand some basic database fundamentals.
Definitions
Before we get into a discussion on Databases, lets establish a common set of terms we will use. The following definitions will be used throughout this course. They are:
- Database
- a collection of data stored in a systematic manner.
- Table
- a collection of records (also called an Entity).
- Record
- a collection of fields.
- Field
- a single piece of data, of a specified type, within a record (also called an Attribute).
- Key
- a field, or group of fields, that uniquely identify a specfic record in a table.
- Index
- a field that will be used to locate a record. Applying indexes to tables can dramatically increase the speed through which queries are completed.
- Relationship
- how tables "relate" to one another.
- Data Type
- how the data is classified (integer, character, date/time, boolean, etc.).
- SQL
- Structured Query Language - common language among popular databases for defining queries.
How to create a Database in Microsoft Access
When Microsoft Access is finished loading, a dialog box pops up which asks you to either create a new database, or select an existing database. When creating a new database, you have two options, to create a Blank database, or create a database from a wizard. If you are creating a database for use on the web, you should create a blank database. Creating a database from a wizard is designed for databases that will run as self contained applications by creating forms, reports, and queries specific to the type of database you choose.
How to create a Database Table
Once the database is created, you will need to build some tables. With the Table tab on top (figure 1.1) click the New button.
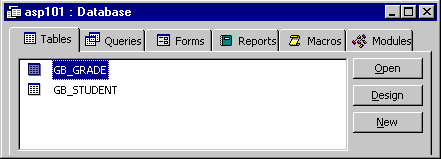 Figure 1.1: Table view menu. |
This will bring up the dialog box illustrated in figure 1.2 The dialog box gives offers 5 options for creating a table:
- Datasheet View - a spreadsheet like view that allows data entry
- Design View - allows detailed table creation. We will use this is perhaps the most used option for creating tables.
- Table Wizard - Steps a user through creating a table. Good start for beginners.
- Import Table - Imports data from an existing Access database, Excel spreadsheet, ODBC Connection, ASCII text file, etc.
- Link Table - Link to an existing Access Database, Excel spreadsheet, ODBC Connection, ASCII text file, etc.
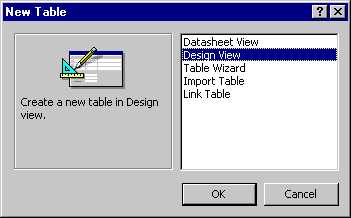 Figure 1.2: Creating a new table. |
When creating a table from scratch, it is best to build the table using the Design View (figure 1.3).
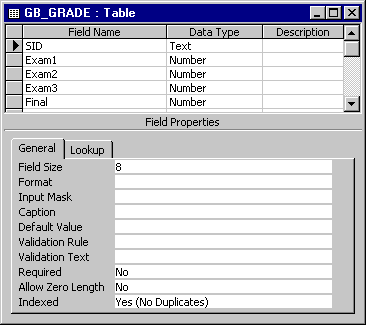 Figure 1.3: Building a table from the table design view. |
In the table Design View, you can add fields, specify data types, key fields (a field(s) that uniquely identifies a specific record). Once you have designed your table, click the Save button located on the standard tool bar. If you haven't defined a primary key, access will tell you this, as well as ask you if you wish to have Access create one for you. Key Values must be unique to each record.
One way to create a key value is to use Access' Autonumber datatype. Autonumbers are integer values that start with 1 and are incremented with each new record you create. Autonumbers cannot be reused if a record is deleted.