Borland Web Server overview
The Borland Web Server executable file (.EXE) is a fully functional web server
with these features:
- HTTP support (version 1.0 plus many 1.1 elements)
- File caching
- Contact (access) logging using the CERN/NCSA
Common Log Format plus transaction logging (see The Borland
Web Server access log for
details)
- Custom MIME types
- Multi-threaded; supports multiple IntraBuilder
sessions
The Borland Web Server acts as an intermediary between
web browsers and URLs, either Intranet or Internet, to transfer requests
and responses between them.
For information on starting up and using the Borland
Web Server, see Using the Borland Web Server.
Using the Borland
Web Server
When you choose to install the Borland Web Server as
part of an application installation, the installation program
copies the web server application and documentation files into
the same directory. The default is C:\Program Files\Borland\Server.
These topics contain information on setting up and using the Borland
Web Server:
Starting and stopping the Borland Web Server
Setting the working directory and basepath
The Borland Web Server window
Customizing the Borland Web Server
The Borland Web Server access log
Saving memory
Starting and stopping the Borland Web Server
To start the Borland Web Server, double-click its icon in its
program group or Windows Explorer. When started, it
appears as an icon or minimized window button at the bottom of the
Windows Desktop:

When started and active, the Borland Web Server is ready to handle client
browser requests. If you're using a compatible application such as IntraBuilder or
Paradox, the web server finds application data by checking the Windows registry. If
you want to access data that is not automatically entered in the registry, you need to
enter a working directory or base path, so the web server will know where to look
for requested information. See Setting the working directory and basepath for details.
Deactivating the web server
To deactivate, or suspend, the Borland Web Server, right-click its icon or minimized
window button at the bottom of the Windows Desktop and choose Shutdown.
Reactivating the web server
To reactivate the Borland Web Server, right-click its icon or button on the
Windows Desktop and choose Startup.
Terminating the web server
To terminate the Borland Web Server and remove its icon or button from the bottom of the Windows Desktop, right-click the icon or button and choose Exit.
Restarting the web server
Once you exit and close the Borland Web Server, you can open it again by clicking its icon in the Windows Explorer or the Borland Web Server program group.
Viewing the web server connection list
By default, the web server is minimized so you can't see its connection history list.
For information on viewing the Borland Web Server connection list,
see The Borland Web Server window.
Setting the working directory and base path
Any requests for IntraBuilder files (with extensions .isv, .jfm, .jrp, or .js) are received by the Borland Web Server, then handled by IntraBuilder.
IntraBuilder looks for these documents in its working directory, so be sure IntraBuilder points to the desired URL path containing these documents.
Choose View|IntraBuilder Explorer or Properties|Desktop Properties in
IntraBuilder to enter the path in the appropriate text box.
Requests for Paradox HTML documents are also handled automatically by the Web Server.
Requests for documents with other extensions are handled only by the Borland Web Server. Be sure the Borland Web Server points to the appropriate web site base path for those documents.
If you have not already set the base path in a popup dialog box, set it on the web
server Pages property page.
The Borland Web Server window
Opening the Borland Web Server window
When you run the Borland Web Server, you have a fully
functional web server that can pass information between a client
web browser and IntraBuilder. To open the Borland Web
Server window and display a list of active and completed connections:
- Right-click the Borland Web Server
icon or minimized window button at the bottom of your Windows
Desktop and choose View Connections.
The Borland Web Server window appears.
Window features
The Borland Web Server window contains a menu bar,
a toolbar,
a connection list,
and a status bar.
The window looks like this before any connections have occurred:
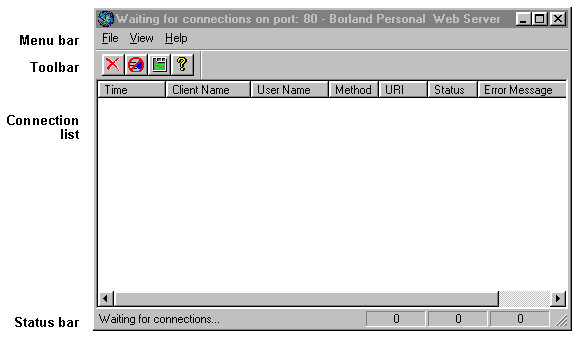
The Borland Web Server menu bar
The Borland Web Server menu bar offers three main commands: File, View, and Help.
- File|Properties
- Displays the Borland Web Server property sheet for customizing
features and performance.
For more information, see Customizing the Borland
Web Server.
- File|Shutdown/Startup
- Deactivates and reactivates the Borland Web Server. This command is a toggle; it changes according to the state of the server.
- File|Exit
- Terminates and closes the Borland Web Server.
- View|Toolbar
- When checked, displays the toolbar beneath the menu bar at the top of
the Borland Web Server. This command is a toggle.
- View|Status Bar
- When checked, displays the status bar at the bottom of
the Borland Web Server window. This command is a toggle.
- View|Clear View Window
- Clears all entries from the connection list; useful when debugging.
- Help|Help Topics
- Displays the online Help file for the Borland Web Server, the
WinHelp version of this HTML file.
- Help|About Web Server
- Displays copyright and other information about the Borland
Web Server.
The Borland Web Server toolbar
The Borland Web Server toolbar contains these buttons,
which are all shortcuts for menu commands:
 | Shutdown/Startup -- a toggle that deactivates and reactivates the
Borland Web Server. |
 | Clear -- clears the web server connection history list. |
 | Properties --
displays the Borland Web Server property
sheet for customizing features and performance. For more
information, see Customizing the Borland Web
Server |
 | Help --
displays the online Help file for the Borland Web Server, the WinHelp equivalent of this file. |
The Borland Web Server connection
list
When a web browser contacts the Borland Personal
Web Server with an HTTP request, the server displays the following
information:
- Time
- Contact time, in local time
- Client Name
- The client Host Name (machine name) if Enable Client Name
Lookup is checked on the web server Status property page; otherwise,
the client's IP Address.
- User Name
- The user ID, entered in response to a browser prompt
- Method
- HTTP method used in the request: GET, POST, or HEAD
- URI
- The named resource (such as an HTML file) the browser is
requesting; this can include the path with respect to the
Base Path set on the web server
Pages property page
- Status
- The HTTP connection code for the current status of the
contact
- Error Message
- An error message
Dead connections only show if Show Completed Connections is checked
on the web server Status
property page.
The Borland Web Server status
bar
To display status messages on the status bar at the bottom of
the Borland Web Server, check Enable Server Status Bar
on the web server Status
property page.
When this setting is checked, the first number at the right end
of the server status bar shows the number of current connections,
the next number shows the total number of connections, and the
third number shows the number of failed connections.
Customizing the Borland Web
Server
To set the Borland Web Server's properties:
- Right-click the Borland Web Server icon
or minimized window button at the bottom of your Windows Desktop
and choose Properties, or
- Choose File|Properties from the web
server menu bar, or
- Click the Properties button on the web server
toolbar
For details, see About Borland Web Server properties.
One important property to set is Base Path, on the Pages property
page. This property sets the root directory where target web pages
are stored (NOT the computer's root directory).
Saving memory
It is convenient to have a lot of threads waiting for client connections,
but this can use a lot of memory. To reduce the number of waiting
threads, you can enter a lower value for Min Ready Connections
on the web server Server
property page.
The Borland Web Server access
log
The access log contains a record of all completed requests to
the Borland Web Server, regardless of returned HTTP status.
Requests that were interrupted by the browser or by network errors
are not logged in the access log.
Activating the log
To start logging server access records, check Enable Access Logging
on the web server Logging
property page and enter a log file name in the Access File Name
text box.
(Note: You can log transactions as well as access records
by setting the appropriate debug logging properties on the Logging
property page.)
Format
The access log complies with the the NCSA/CERN Common Log Format
(CLF). A sample entry is shown below (each entry is on a single
line in the actual log file):
146.82.56.219 - - [23/Apr/1996:05:28:13 -0800] "GET /newinfo/32srvr/newpage.html
HTTP/1.0" 200 29764
A dash or minus means null or not applicable.The fields are (in
order):
- IP address or host name of the client. For host-name
logging, Enable Client Name Lookup must be checked on the web
server Status property
page. This slows down server performance and is not recommended.
- Unused (placeholder for RFC931/TAP identification;
deprecated, not supported).
- Authenticated user name. Present only if the
browser sends basic authentication header with the request.
- Date/time per Common Log Format. Local time,
with GMT offset
- Quoted string containing the HTTP request line,
including method, URL, and HTTP version fields.
- The HTTP/1.0 status/result code for the request.
- The number of bytes, exclusive of HTTP header
bytes, returned to the client as a result of the request.
About Borland Web Server properties
To set Borland Web Server properties:
- Right-click the Borland Web Server icon
or minimized window button at the bottom of your Windows Desktop
and choose Properties, or
- Choose Configuration|Properties from the web
server menu bar, or
- Click the Properties button on the web server
toolbar
When the tabbed property sheet appears, click a page tab to set
each kind of property:
-
Server properties indicate how the Borland Web Server handles
connections
-
Pages properties indicate
the location of web pages accessed by the Borland Web
Server
-
Logging properties indicate whether you want to keep log files of connections
and transactions and the names of these files, if kept
-
MIME properties show records in the Borland Web Server MIME
Types database (you can add, edit, and remove MIME media-type
records on the MIME property page)
-
Status properties control client identification detail and status display
Web Server Properties dialog
box (Server page)
The settings on this box control how the Borland Web
Server handles connections.
Dialog box options
HTTP Port
The port the server listens to for connections; no two servers
can have the same port on the same machine. Values are 1 to 32767;
default = 80.
Min Ready Connections
The number of threads to prepare for connection at startup and
keep waiting after startup. The number must be equal to or less
than Max Connections. A higher number speeds connections but uses
much more memory. Values are 0-255 (Default = 25).
Max Connections
Total number of connections allowed at one moment. Values are
1-255 (Default = 100).
Connection Timeout
The number of seconds to wait before issuing a time-out and breaking
the connection. This property is used in both reading requests
and sending responses. It also specifies how long to keep a keep-alive
connection open. Values are 1-600.
Keep Alive Connections
Allow Keep Alive Connections
If checked, permits a request to keep the connection open. This
allows a browser quicker access on its second request; it doesn't
need to wait for a connection to open.
Checking Allow Keep Alive Connections uses up more of the server's
available connections.
Max Requests Per Connection
The number of request/response transactions allowed for each keep-alive
connection (if Allow Keep Alive Connections is checked). Values
are 1-1024 (Default = 5).
Web Server Properties dialog
box (Pages page)
The settings on this page indicate the location of web pages accessed
by the Borland Web Server.
Dialog box options
Base Path
The root directory where the web pages are stored. (Caution:
For security reasons, don't use your own root directory. Choose
a directory with only subdirectories that users are allowed to
access. [xxx add examples for these properties.]
Default Page
The default web page name in each directory.
Footer Page
The full path plus a page with the information to appear at the
bottom of each transferred page; like a template for the page
footer.
Header Page
The full path plus a page with the information to appear at the
top of each transferred page; like a template for the page header.
Web Server Properties dialog
box (Logging page)
The settings on this page indicate whether you want to keep log
files of connections and transactions and the names of these files,
if kept.
Dialog box options
Access Logging
These settings enable and name a log file of who connected to
the server. The access log file is written in Common Log Format.
For more information, see The Borland Web Server access log.
Enable Access Logging
When checked, logs connection history to a file in Common Log
Format.
Access File Name
When checked, logs connection history to a file in Common Log
Format.
Debug Logging
These settings enable and name a debug log file of debug information
for transactions handled by the server.
Enable Debug Logging
When checked, logs debug information for transactions to a file
for later tracing and debugging.
Debug File Name
The name of the Debug Log file where transaction records are stored
for later tracing and debugging.
The log includes the buffer received from the browser, the buffer
sent to the browser, and a dump of the variables from both the
request and response.
Web Server Properties
dialog box (MIME page)
This page displays records in the Borland Web Server
MIME Types database. You can use the buttons to add, edit, and
remove MIME media-type records.
Add
Displays the New MIME Type dialog box where you can enter a file
extension with associated media type and subtype.
Extension
The extension used for a certain media type -- for
example, txt.
MIME Type
The main media type associated with Extension -- for
example, text.
MIME Subtype
The category of the main media type associated with Extension -- for example, plain.
Edit
Displays the Change MIME Type dialog box where you can change
the MIME Type or MIME Subtype associated with the selected extension.
Remove
Deletes the selected extension's record.
Web Server Properties dialog
box (Status page)
The settings on this page control client identification detail
and status display.
Dialog box options
Enable Client Name Lookup
If checked, attempts to convert an IP address to an Internet machine
name. This takes more time than when Enable Client Name Lookup
is not checked, but more connection information is obtained.
Enable Server Status Bar
When checked the server status bar shows information about the
current status of the server and its connections. Enable Server
Status Bar must be checked before these updates are made, but
updates are independent of other properties.
Show Active Connections
When checked, active threads appear in the server list (state
= New/Recv, Processing, Sending).
Show Completed Connections
When checked, completed thread connections (status = Dead) appear
in the server list.
NumberOf Completed Connections
If Show Completed Connections is checked, the number of connections
with status = Dead to show in the Borland Web Server
connection list.