Introduction |
Table I.1 contains the artwork symbols used in this volume. You can use it as a resource as you study the diagrams in this guide.
Table I.1 Artwork Symbols
| Symbol | Meaning | Symbol | Meaning | Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
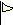 |
Access token. An object that contains user information and is used for security purposes. |
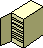 |
Automated Library. Tape/disk libraries that contain a collection of media and one or more drives. |  |
Client. A computer that accesses shared network resources provided by another computer. |
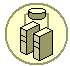 |
Cluster. A group of independent computers that works together as a single system. |
 |
Database. Any collection of data organized for storage and access by computers. | 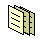
 |
Document. Any self-contained piece of work created with an application program and saved on a disk. |
 |
Domain. In Windows 2000, a collection of computers defined by the administrator that share a common directory database. | 

 |
E-mail. The exchange of text messages and computer files over a communications network. | 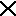
 |
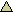
Failure. The inability of a computer system or related device to fail gracefully over a period of time. |
 |
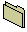
File Folder. A directory or subdirectory. | 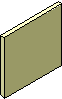 |
Firewall. A piece of a security system used to prevent unauthorized access to a network. |
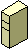 |
Generic Server. A computer running administrative software. |
 |
Hard Disk. A device used for storing data magnetically. | 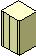 |
Host. The main computer in a system of computers or terminals connected by communications links. |
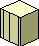 |
Host. The main computer in a system of computers or terminals connected by communications links. |
 |
I/O Filter. A series of definitions that indicate to a router the type of traffic allowed on each interface. |
 |
Internet. Refers to the worldwide collection of networks that communicate with each other. |  |
Laptop or Portable Computer. A small, portable personal computer. |
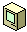 |
Macintosh Client. A networked personal computer manufactured by Apple Computer Corporation. |
 |
Mainframe Computer. A high-level computer designed for the most intensive computational tasks. |  |
Mainframe Computer. A high-level computer designed for the most intensive computational tasks. |
 |
Mixed mode domain. A mode in which Windows 2000 and Windows NT domain controllers coexist in a domain. |  |
Modem. A communications device that enables a computer to transmit information over a standard telephone line. |
 |
Modem Bank. A collection of modems connected to a single server. |
 |
Network Adapter. An expansion card or other device for connecting a computer to a local area network. |  |
Organizational unit. A structure within a domain. |  |
Organizational unit. A logical container holding users, groups, computers, and other organizational units. |
 |
Packets. A network transmission unit of fixed maximum size. |  |
Printer. A print device that is directly connected to your network. |
 |
Remote Access connection. A dial-up connection between servers, domain controllers, and sites. |
 |
Root. The highest or uppermost level in a hierarchically organized set of information. |  |
Router. An intermediary device that directs and optimizes network traffic. |
 |
Security Key. A security descriptor that contains the local security policy, such as specific user rights. |
 |
Server Farm. A group of servers that provides services to the network. |  |
Site. One or more well-connected TCP/IP subnets. |  |
Steelhead router. A computer acting as an intermediary device on a communications network. |
 |
Switch or Gateway. A device connecting two networks that is capable of passing or blocking packets. |
 |
Tape or Tape Backup. A tape cartridge format used for data backups. |  |
Tape Drive. A device for reading and writing tapes. |
 |
Terminal. A device consisting of a video adapter, a monitor, and a keyboard that does little processing on its own and is connected to a computer via a communications link. |
 |
Tunnel. The logical path by which the encapsulated packets travel through the transit internetwork. |  |
Windows NT domain. A networked set of computers that runs Windows NT 4.0, that shares a SAM database, and that can be administered as a group. |
 |
Windows 2000 Server. A server that provides centralized management on the network. |
 |
Uninterruptible power supply. A device between a power source and a computer that ensures electrical flow is not interrupted. |