e.g. to enter 12 degrees 34.5 minutes do this 12<space>34.5
for the time 12:45:56 12<space>45<space>56
All times are in UTC (universal time coordinated).

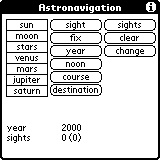
On the left are the celestial bodies the program can use while centre and left display the operations the program can perform.
To reduce a sight or calculate a fix choose a star (from the left column) and start the calculation of your first sight (select 'sight').
Example:
We will reduce two sights and calculate the fix using the following sample data. (Please set the year for the examples to 1990.)
D.R. 13 53' N 44 39' W 1. sight sun 16.12.1990 UTC 10:49:06 down 19 18.6' no index error height 2 m 2. sight sun 16.12.1990 UTC 14:37:10 down 52 28.2' no index error height 2 m run distance course 270 , 19 nmThese are sun sights so select 'Sun' and then 'Sight' from the main menu.
Now you can input your data for the first sight. First input your D.R. (Dead Reckoning) position. Remember the input terms: first the degrees then a space followed by the minutes.
Then select north or south. North is the default.
Do the same with the longitude. Use the 'old' button to input an old fix or destination in these fields.
The date follows. Please input only month and day. The year is set in the main menu.
The time is the next data. Please remember the input terms.
Now input the sextant angle. If you work with the sun or the moon select the type of sight.
Input the correction now. The defaults are typical for sailors. If your index error is negative, you have to put an '-' in front of the minutes. The height of the eyes are in metres.
The buttons in the form 'sights' mean:
To change between date format (dd.mm./mm.dd.) or the height (m/ft) press the menu button and select your favorite.
Now push the 'compute' buttom.
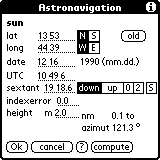
Please wait for the computing. You will see the miles away or towards the star and the computered azimut. The miles should be very small. If the value seems too big there will be an input error or your sextant angle needs to be controlled. If everything is ok press the 'Ok' buttom. You are back to the main menu now.
For the second sight you can choose all stars again. The mask (inpout form) is like the first one but there is no position. You have to input the running values angle and distance.
The new sight is computed from the new position.
After two sights you can visit your position. Please press the 'fix' buttom in the main menu. The output looks like this:
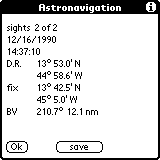
The D.R. is shown from your last postion. The correction is computed (BV) from here.
You may save your values to the memopad as a log file.
You can add now another sight or clean up everything. If you do nothing the sight will be saved so when you start the program again you still have this position. More examples are below in this document.
The other inputs are the same as for the sun.
For example:
D.R. 13 55 N 44 31 W 1. sight unknown star 16.12.1990 UTC 8:26:10 bearing 80 sextant 44 36.4' 2. sight unknown star 16.12.1990 UTC 8:30:30 bearing 350 sextant 42 4.4' no run distance
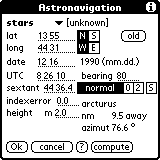
The program always computes all stars if unknown is selected. Selection is then made from the nearest of the 80 stars or planets but only you can determine if the output is correct or not.
The output for this example should be:
2 sights 16.12.1990 8:30:30 pos lat: 13 55.0 N long: 44 31.0 W fix lat: 13 49.6 N long: 44 39.8 W BV 237,5 10.1 nmThe stars in this case are Arcturus and Dubhe.
You can try an other sight (upto 20):
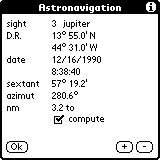
3. sight unkown star 16.12.1990 UTC 8:38:40 bearing 270 sextant 57 19.2' no index error, height 2 m no run distanceThe output is:
3 sights 16.12.1990 8:38:40 pos lat: 13 55.0 N long: 44 31.0 W fix lat: 13 48.8 N long: 44 37.6 W BV 225.9 8.8 nmThe unknown star was now the planet Jupiter.
There are no Greek characters for stars in the program I have used th following:
a alpha e epsilon i iota n nu r rho v phi b beta f zeta k kappa q xi s sigma x chi c gamma g eta l lambda o omicron t tau y psi d delta h theta m mu p pi u upsilon z omega
If you do this with the above example and deactivate the third star then the fix must be the same as you got from the first two sights.
D.R. 15 30 N 38 40 W 1. sight sun down 13.12.1990 UTC 10:46:29 sextant 23 6.6' 2. sight sun down 13.12.1990 UTC 14:00:14 sextant 51 0.8' no index error, height 2 m run distance 260 und 16 nmYour fix should be
14 50.7 N 39 23.6 WPress Change on the main menu. The 2nd sight is now the first sight in a new sequence with the fix becoming the D.R.position. The miles away or towards should be very short.
Here is the new sight:
sun down 13.12.1990 18:08:24 sextant 24 59.6' no index error, height 2 m run distance 260 und 24 nmThe fix is now:
14 46.3 N 39 48.0 W
Most navigators like to prepare their sextant before taking a sight. To do this input the data as usual. However you cannot input the sextant angle as you don't know it yet. Press the '?' to get the value. If you do this with a star you also will get a bearing.
For example: You want to go from your last fix to St. Lucia. Choose the 'course' buttom in the main menu. As you have previously taken a fix you can select the fix data by pressing 'old'. Then you only have to put in your destination data.
pos: lat: 14 46.3 N long: 39 48.0 W target: lat: 14 2.0 N long: 61 1.0 W course 270.6 distance 1233.3 nm
If you ever used a target before your may recall it by pressing the 2nd 'old' button.
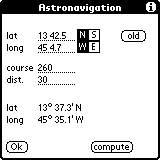
Using the same example for this you sailed 30 miles with the
course 260 degree.
If you have calculated a fix before you may recall it now (press the 'old' button).
The result also is saved and may by similarly recalled by the 'old' button. In this way you may continue computing destinations.

An example (clear all old sights first):
D.R. 14 0.0 N 56 0.0 W noon at 20.12.90 15:42:00 sextant 52 30.2' Index 0.0' height 2 mThe miles are 9.1 towards.
lat 14 0.0' N - 9.1' --------------------------- lat at noon 13 50.9' NIf you select 'Ok' this will be saved as a new sight.
An example (remember to clear the old data first):
D.R. 16 45.0' N 34 23.0' W 1. sight sun down 11.12.90 10:21:32 sextant 21 8.2 2. sight sun down 11.12.90 10:23:17 sextant 21 29.3 3. sight sun down 11.12.90 10:25:38 sextant 21 55.0 4. sight sun down 11.12.90 10:27:50 sextant 22 30.0 5. sight sun down 11.12.90 10:30:07 sextant 22 51.1 run distance course 250 nm 15 Some more sights: 6. sight sun down 11.12.90 13:30:18 sextant 49 2.0 7. sight sun down 11.12.90 13:34:02 sextant 49 19.0 8. sight sun down 11.12.90 13:37:13 sextant 49 31.4 9. sight sun down 11.12.90 13:40:32 sextant 49 41.2 10. sight sun down 11.12.90 13:44:24 sextant 49 54.6>From 10 sights you get this fix:
16 19.9 N 34 50.7 WNow select 'lines' in the fix page and examine distance values. We will now deactivate the sights with the largest offsets. When you deactivate the sight 4 (5.7 nm) you will get a better standard deviation. Going on with the 6. sight (4.7 nm) the deviation is further reduced.
16 18.2 N 34 53.6 WPlease be careful. The angle between the two azimuths is very low. It's better to have an azimuth value of more then 40 degrees.
for all use index error = 0.0' height = 2 metres 1. D.R. 25 18 N 18 6 W 1. sight sun down 28.11.90 UTC 16.53.02 sextant 16 40.4 2. sight moon up 28.11.90 UTC 16.56.18 sextant 22 35 no run distance new pos. 25 23.3 N 18 15.1 W 2. D.R. 24 23 N 20 20 W 1. sight unknown star 30.11.90 UTC 7.05.42 bearing 120 sextant 32 41.4 2. sight unknown star 30.11.90 UTC 7.12.14 bearing 230 sextant 22 29.8 position 24 5.9 N the star are spica and 20 32.1 W sirius. 3. D.R. 13 43 N 44 31 W 1. sight mars 16.12.90 UTC 21.33.30 sextant 39 29.4 2. sight achernar 16.12.90 UTC 21.38.18 sextant 16 23.2 position 14 38.3 N 44 55.5 W (very bad) 4. D.R. 14 15 N 56 7 W 1. sight venus 25.12.90 UTC 21.56.20 sextant 4 54.2 2. sight vega 25.12.90 UTC 22.01.54 sextant 9 23.8 position 14 4.9 N 56 7.1 W 5. Examples for a running fix D.R. 39 40 N 15 20 E 1. sight sun down 14.07.1990 UTC 5:20:16 sextant 16 20.6 run distance 336 8 nm 2. sight sun down 14.07.1990 UTC 7:26:53 sextant 40 30.0 fix 39 26.0 N please notice the 15 16.8 E very short time between the sights Now change the 2nd sight to become the first position new sight run distance 323 9.4 nm sight sun down 14.07.1990 UTC 9:44:23 sextant 64 54.3 new fix 39 40.7 N 15 10.3 E Now change the 2nd sight to become the first position again new sight run distance 323 7.4 nm sight sun down 14.07.1990 UTC 11:10:22 sextant 71 39.6 new fix 39 46.6 N 15 4.4 E