by Grahame Marsh - grahame.s.marsh@corp.courtaulds.co.uk
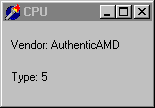
I recently upgraded my motherboard to a 233Mhz AMD processor. I knew that you could provoke an Intel chip into returning the text “GenuineIntel” in a series of registers so I was curious to know what the AMD chip would return. The answer proved to be the text “AuthenticAMD”:

This bitmap was clipped from a simple form which just has two labels that are initialised in the FormCreate event handler:
The VendorId and CpuType values are obtained using the CpuInfo unit listed below. Portions of this are based off of Intels published information on obtaining CPU ID's:
Enjoy!
unit CpuInfo;
interface
type
TFeatures = record
case integer of
0: (RegEAX,
RegEBX,
RegEDX,
RegECX
: integer);
1 : (I : array [0..3] of integer);
2 : (C : array [0..15] of char);
3 : (B : array [0..15] of byte)
end;
const
{$IFNDEF WIN32}
i8086 = 1; // includes
8088/V20/V30/80186/80188
i80286 = 2;
i80386 = 3;
{$ENDIF}
i80486 = 4;
Chip486 = 4;
iPentium = 5;
Chip586 = 5;
iPentiumPro = 6;
Chip686 = 6;
// known vendor id strings:
Intel = 'GenuineIntel';
AMD = 'AuthenticAMD';
var
CpuType : byte = 0;
// type of CPU
VendorId : string [12]= ''; // contains vendor
string
Features : TFeatures;
// contains signature and feature information
procedure LoadFeatures (I : integer);
implementation
{$O-}
const
CpuId = $0a20f; // hardcoded CpuId instruction
// not supported by inline assembler
var
CpuIdFlag : boolean = false; // true if CpuId instruction
works
MaxCPUId : integer;
// contains max value of eax value for CpuId instruction
// procedure to load features from CPUId instruction
// call with eax containing CPUId instruction number
procedure GetF;
asm
dw
CpuId // Hardcoded
CPUID instruction
mov
[Features.RegEAX], eax
mov
[Features.RegEBX], ebx
mov
[Features.RegECX], ecx
mov
[Features.RegEDX], edx
end;
// procedure to clear features record to zero
procedure ClearF;
asm
mov
edi, offset Features // edi point at features record
xor
eax, eax
// clear eax
mov
ecx, eax
mov
cl, 4
// 4 double words, 16 bytes
cld
// forward direction
rep
stosd
// do it
end;
// This procedure determines the type of processor in a system
// and sets the CpuType variable with the appropriate
// value. If the CPUID instruction is available, it is used
// to determine more specific details about the processor.
// All registers are used by this procedure, none are preserved.
// To avoid AC faults, the AM bit in CR0 must not be set.
procedure CheckOutCpu;
asm
{$IFNDEF WIN32}
// 8086 processor check
// Bits 12-15 of the FLAGS register are always set on the
// 8086 processor.
pushf
// push original FLAGS
pop
ax
// get original FLAGS
mov
cx, ax // save original
FLAGS
and
ax, 0fffh // clear bits 12-15 in FLAGS
push
ax
// save new FLAGS value on stack
popf
// replace current FLAGS value
pushf
// get new FLAGS
pop
ax
// store new FLAGS in AX
and
ax, 0f000h // if bits 12-15 are set, then
cmp
ax, 0f000h // processor is an 8086
mov
[CPUType], 1 // set flag to 8086/8088
je
@@2
// jump if processor is 8086/8088
// 286 processor check
// Bits 12-15 of the FLAGS register are always clear on the
// 286 processor in real-address mode.
or
cx, 0f000h // try to set bits 12-15
push
cx
// save new FLAGS value on stack
popf
// replace current FLAGS value
pushf
// get new FLAGS
pop
ax
// store new FLAGS in AX
and
ax, 0f000h // if bits 12-15 are clear
mov
[CPUType], 2 // processor=80286, turn on 80286 flag
jz
@@2
// if bits set, processor is 80286
// 386 processor check
// The AC bit, bit #18, is a new bit introduced in the EFLAGS
// register on the 486 processor to generate alignment faults.
// This bit cannot be set on the Intel386 processor.
pushfd
// push original EFLAGS
pop
eax
// get original EFLAGS
mov
ecx, eax // save original EFLAGS
xor
eax, 40000h // flip AC bit in EFLAGS
push
eax
// save new EFLAGS value on stack
popfd
// replace current EFLAGS value
pushfd
// get new EFLAGS
pop
eax
// store new EFLAGS in EAX
xor
eax, ecx // can't toggle AC bit,
processor=80386
mov
[CPUType], 3 // turn on 80386 processor flag
jz
@@2
// jump if 80386 processor
push
ecx
popfd
// restore AC bit in EFLAGS first
{$ENDIF}
// 486 processor check:
// Checking for ability to set/clear ID flag (Bit 21) in EFLAGS
// which indicates the presence of a processor with the CPUID instruction.
mov
[CPUType], 4 // turn on 80486 processor flag
mov
eax, ecx // get original EFLAGS
xor
eax, 200000h // flip ID bit in EFLAGS
push
eax
// save new EFLAGS value on stack
popfd
// replace current EFLAGS value
pushfd
// get new EFLAGS
pop
eax
// store new EFLAGS in EAX
xor
eax, ecx // can't toggle ID bit,
je
@@2
// processor=80486
// higher than 486 check:
// Execute CPUID instruction to determine vendor, family,
// model, stepping and features. For the purpose of this
// code, only the initial (0) set of CPUID information is saved.
mov
[CPUIdFlag], 1 // flag indicating use of CPUID inst.
push
ebx
// save ebx register
mov
eax, 0 // set up
for CPUID instruction
dw
CpuId // Hardcoded
CPUID instruction
mov
[MaxCPUId], eax // keep max value
// get and save vendor ID
mov
[byte ptr VendorId], 12
mov
[dword ptr VendorId+1], ebx
mov
[dword ptr VendorId+5], edx
mov
[dword ptr VendorId+9], ecx
// get family/model/stepping/features
call
ClearF
mov
eax, 1
call
GetF
// get feature stuff
shr
eax, 8 // isolate
family
and
eax, 0fh
mov
[CPUType], al // set CPUType with family
@@1: pop
ebx
// restore ebx register
@@2:
end;
// requires that a call has been made to CpuId procedure to set
flags correctly
procedure LoadFeatures (I : integer);
asm
call
ClearF
cmp
[CpuIdFlag], 0 // test if CPUId instruction valid
je
@@1
mov
eax, [I] // test if argument
in range
cmp
[MaxCpuId], eax
jl
@@1
call
GetF
// ok let's do it
@@1:
end;
initialization
CheckOutCPU;
end.