Glossary

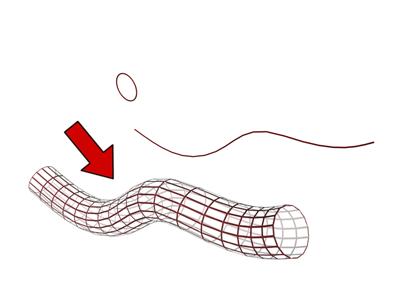
A circle is lofted along a path to construct a tubular shape.
Lofting is an important method for 3D object creation. You create shape objects to serve as a path and any number of cross-sectional shapes. The path becomes the framework that holds the cross-sections forming your loft object.
Once you create a loft object you can change and animate its parameters and sub-objects:
Add and replace cross-section shapes or replace the path.
Change or animate the parameters of the path and shapes.
Change or animate the surface parameters of the loft object.
The lofting process first requires that you create shape objects to serve as the path and cross-sections of your loft object.
The term lofting comes from early shipbuilding. A large framework called a loft was built to hold the hull of a ship while it was assembled. The process of hoisting the ribs (cross-sections) of the hull into the loft became known as lofting.
A traditional method for building three-dimensional models of a modern vehicle design is to draw cross-sections at a number of key points. These cross-sections are cut out to form two-dimensional templates that are then placed on a rail. The model builders fill in the space between the templates to generate the surface of the model.
You create loft objects using a similar process. You first create two or more spline objects. One of these splines will be the rail, which is referred to as the path. The rest of the splines are the cross-sections of your object, which are called shapes. As you arrange your shapes along the path, the software generates a surface between the shapes.